Your Pain Meds’ Side Effects May Be Masquerading as Heart Failure
Matthew Growdon's study finds "prescription cascades" where drug side effects lead to unnecessary second prescriptions, causing further harm and costly hospitalizations.

University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSFMatthew Growdon's study finds "prescription cascades" where drug side effects lead to unnecessary second prescriptions, causing further harm and costly hospitalizations.

Scientists have thought that when we hear language, the brain processes it the same way, whether it's familiar or foreign. A new study reveals that exposure to a language changes how certain clusters of neurons respond to the familiar sounds. From those changes, we develop the understanding of syllables, words, and syntax.
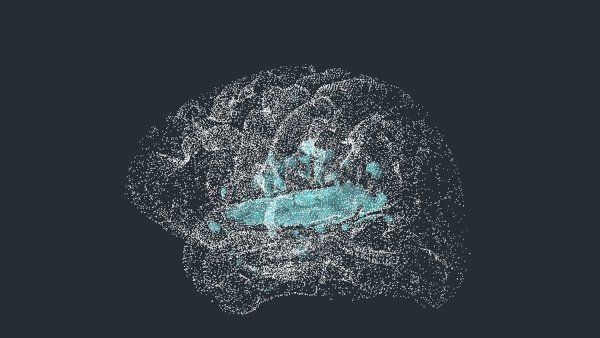
UCSF researchers used AI to personalize Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Parkinson's gait problems, leading to meaningful, customized improvements in walking and mobility—a major breakthrough for patients.

Neurologist Dr. Ptacek explains how "falling back" disrupts the 24-hour circadian clock, affecting mood and performance, with mitigation tips.

Martin Kampmann’s work, supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), maps cellular “decision points” that determine whether brain cells survive or die, laying the groundwork for treatments that intervene before irreversible brain damage occurs from dementia.
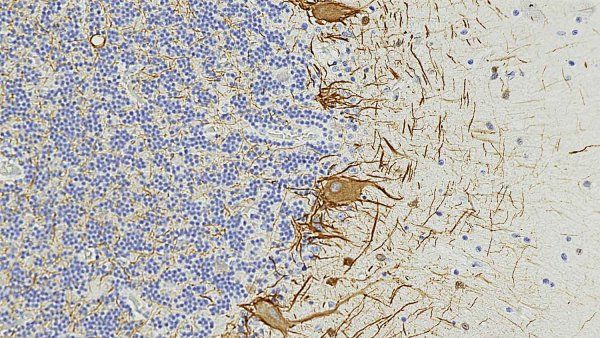
Image In the human brain, neurofilament light chain (NfL, shown in brown) is seen in brain cells and the neural wires that connect them. UCSF
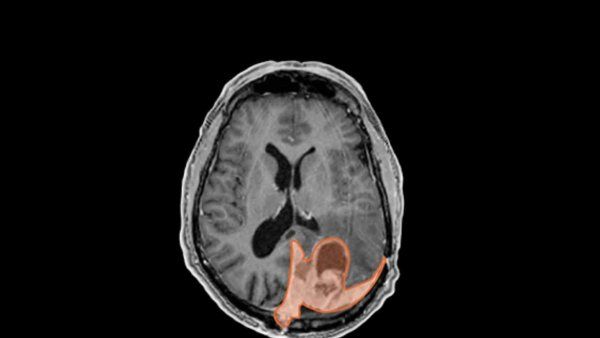
UCSF radiation oncologist David Raleigh, MD, PhD, studies the link between brain tumors and injectable birth control.
Generalized anxiety disorder affects 1 in 20 U.S. adults. Those with serious symptoms may isolate themselves to the point that they rarely leave their home.

Vikram Rao, director of the UCSF Epilepsy Center, discusses why a third of seizure patients don’t respond to medication and the promising new surgical and technological treatments available.

UCSF scientists discovered that an overlooked cell type in the brain plays a central role in healing traumatic brain injury. Understanding how it does this will lead to treatments for injuries that currently have only minimal interventions.
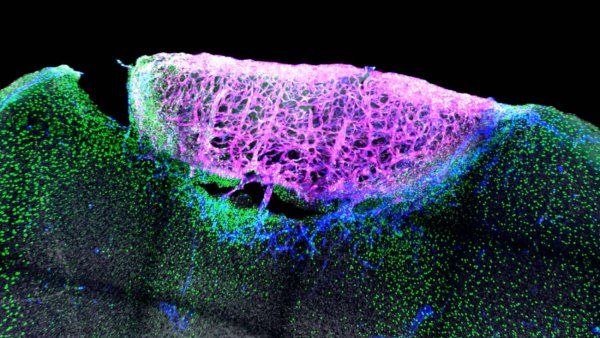
A study screened dyes found in textiles and in the laser industry that can be used in imaging for preclinical studies to diagnose and differentiate between neurodegenerative diseases. Currently, dyes used in mouse studies cannot distinguish between different types of dementia.
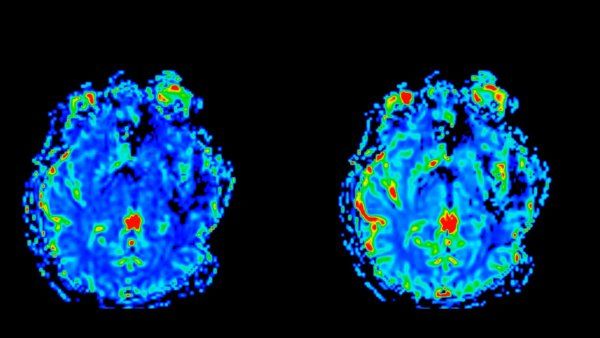
UCSF looks back on four ways it pioneered deep brain stimulation with the help of federal funding, helping patients with Parkinson’s Disease, chronic pain, depression, and more.

Scientists discover a protein that gets concentrated in the brain during aging, leading brain connections to wither and cognitive decline to accelerate - and a way to counter its effects.
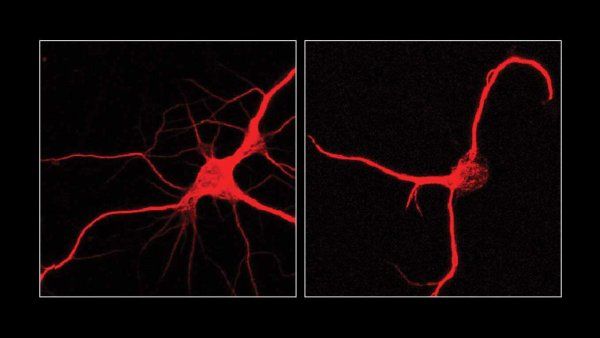
Two new Pew Latin American fellows, Beatriz De Moraes, PhD, and Lilian Gomes de Oliveira, PhD, will each receive a $30,000 annual stipend for two years to support their work at the crossroads of immunology and neuroscience.

Researchers discovered that a different part of the brain handles stringing sounds and words together into coherent sentences. The information could help people who have had strokes and lost the ability to create sentences.
Microglia, a type of brain immune cell, can gobble up amyloid beta protein, which clumps together into toxic aggregates during Alzheimer's disease.
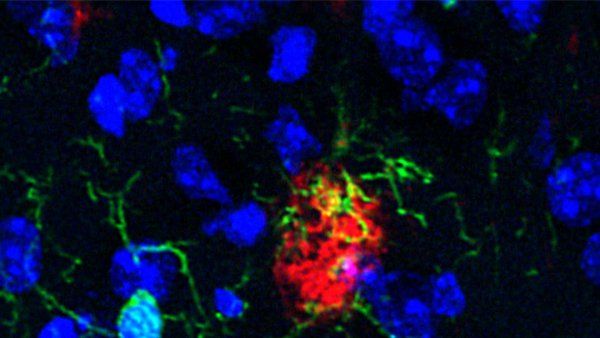
Scientists at UCSF and Gladstone Institutes have identified cancer drugs that promise to reverse the changes that occur in the brain during Alzheimer’s, potentially slowing or even reversing its symptoms.

For patients with Parkinson's disease, changes in their ability to walk can be dramatic. “Parkinson’s gait,” as it is often called, can include changes in step length and asymmetry between legs. This

The Byers Award recognizes outstanding research by faculty members in the middle of their careers. Martin Kampman’s honorary 2025 lecture is titled “A CRISPR approach to neurodegenerative diseases.”

Visual auras, like those that occur in migraines, may be signs of small injuries to the brain’s visual cortex, according to a clinical trial at UC San Francisco that tracked the appearance of these

It’s been recognized for some time that Alzheimer’s disease affects brain regions differently and that tau — a protein known to misbehave — plays an important role in the disease. Normally, tau helps

An expert in cognitive neuroscience shares the ways that music may help flex our neurons, plus her top tips for a music-filled life.

Neuroscientist Grae Davis, PhD, unpacks why public understanding of science matters.

Scientists are working to rewire the brain’s pain pathways and unlock lasting relief.
