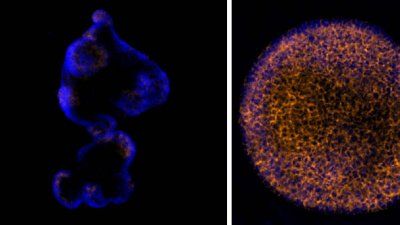
Replacing Myelin Protects Nerve Cells, Restores Function in Mouse Model of Multiple Sclerosis
Using a mouse model of multiple sclerosis, UCSF scientists demonstrated that regenerating myelin can both protect neurons from damage and restore lost function.