Scientists Discover a New Hormone that Can Build Strong Bones
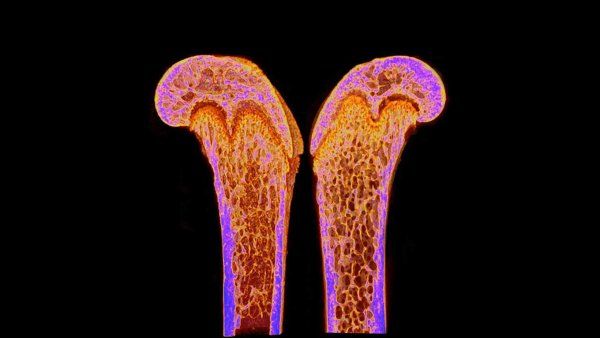
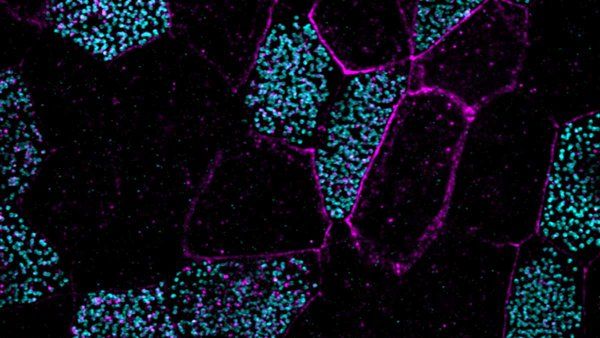
A newly discovered hormone explains why females can maintain bone density during lactation, when calcium is stripped away to make milk. This discovery could one day have applications to treating fractures, osteoporosis, and other bone diseases.