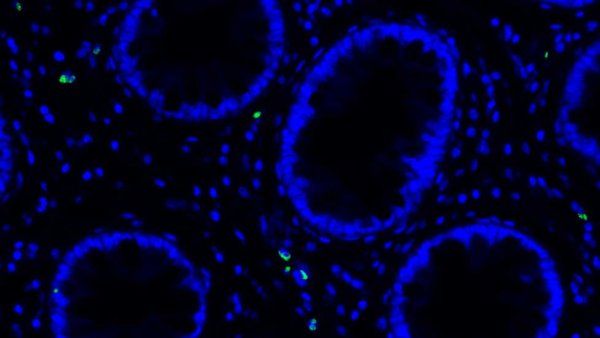
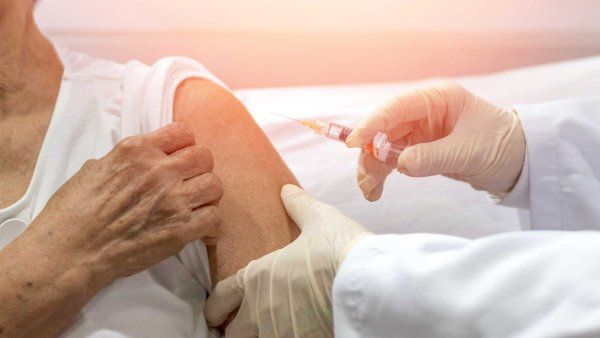
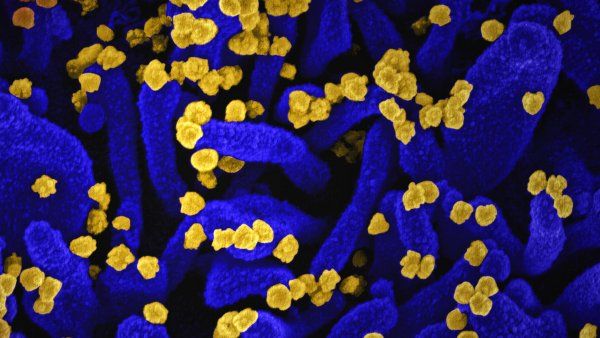
What to Know About Long COVID and How to Reduce Your Risk
Researchers Micheal Peluso and Valerie Flaherman answer questions about what we know about one of COVID’s most enduring mysteries, including how to potentially reduce your risk and who is most likely to develop long COVID.