Can a Leading Laboratory Unlock the Cause of Gastrointestinal Disease?
Faranak Fattahi’s lab is a national leader in growing stem cells to model peripheral nerves, focusing on gastrointestinal diseases.

University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSFFaranak Fattahi’s lab is a national leader in growing stem cells to model peripheral nerves, focusing on gastrointestinal diseases.

Sleep medications may increase risk of dementia for white people, though the type and amount of medication may also explain the higher probability.

Could psychedelics become mainstream medicines?

Resecting brain tumors called gliomas as much as possible soon after diagnosis offers a distinct survival advantage when looking at the disease trajectory 10 years later, find UCSF researchers.

UCSF experts discuss the current state of Alzheimer’s treatments and future therapies that may slow progression of the disease.
While we sleep, our brains process our daily actions to create motor memory, which makes physical acts such as throwing a basketball subconscious.

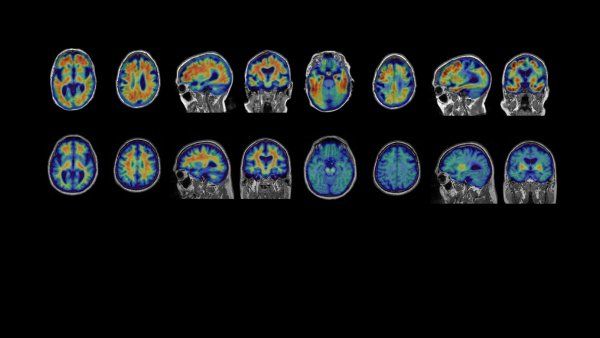
UCSF Experts Present Research at the Annual Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) Conference in San Francisco.
The brains of people with Down syndrome develop the same neurodegenerative tangles and plaques associated with Alzheimer’s disease and frequently demonstrate signs of the neurodegenerative disorder in their forties or fifties. A new study shows that these tangles and plaques are driven by the same amyloid beta (Aß) and tau prions as Alzheimer’s disease.

Brain implants for speech, neurological effects of COVID-19, and motor recovery after stroke are among the topics that researchers from UCSF will be presenting at this year’s annual meeting of the Society for Neuroscience.
A $147 million grant will expand diversity among Alzheimer’s disease research participants, and involve partners from UCSF, the San Francisco VA Medical Center, and the Northern California Institute for Research and Education.

A small molecule called ISRIB that was identified at UCSF can reverse the neuronal and cognitive effects of concussion in mice weeks after an injury occurred, new research found.
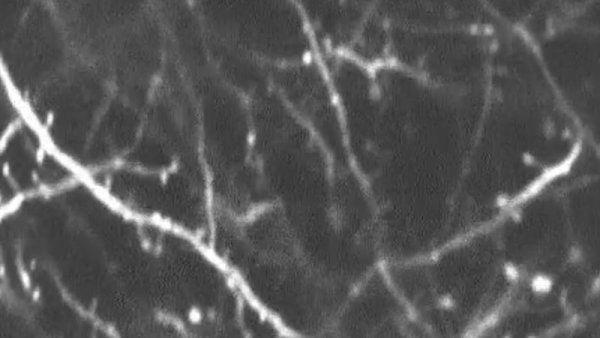
After a decade of work, scientists at UCSF’s Neuroscape Center have developed a suite of video game interventions that improve key aspects of cognition in aging adults.
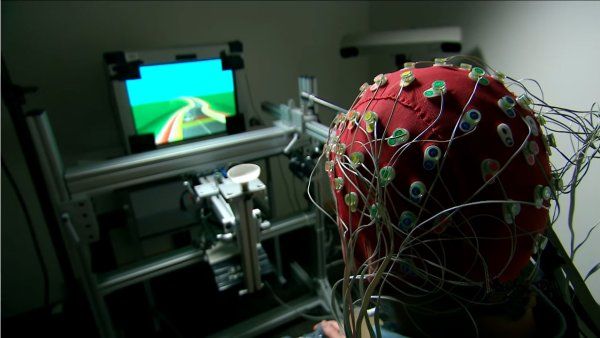
A new study shows that fewer Black, Hispanic and Asian patients would qualify for these treatments that may slow Alzheimer’s progression, since cognitive impairment in these groups is more likely to be caused by other forms of dementia that may be unrelated to amyloid plaques.
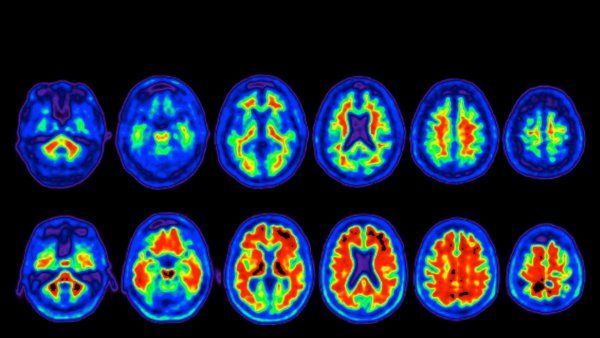
UCSF has revealed how blood vessel cells develop in the prenatal human brain, paving the way to fully understand the role of these cells in healthy brain development and disease.

Scientists have designed compounds that hit the same key receptor that LSD activates without causing hallucinations. A single dose produced powerful antidepressant and antianxiety effects in mice that lasted up to two weeks.
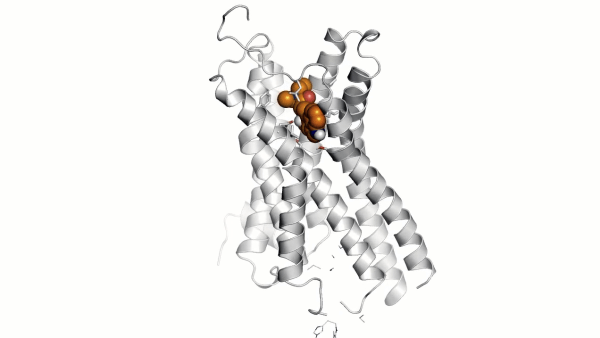
Researchers have found significant differences between the gut bacteria profiles of multiple sclerosis (MS) patients and healthy individuals, showing new pathways for potential treatment.
The study, funded by the National Institute on Aging, recruited people who were 50 and older and homeless, and followed them for a median of 4.5 years. By interviewing people every six months about their health and housing status, researchers were able to examine how things like regaining housing, using drugs, and having various chronic conditions, such as diabetes, affected their risk of dying.

The discovery of how to shift damaged brain cells from a diseased state into a healthy one poses a potential new path to treating Alzheimer’s and other forms of dementia, according to a new study from UCSF researchers.
Blood tests taken within 24 hours of a traumatic brain injury (TBI) flag which patients are likely to die and which patients are likely to survive with severe disability, according to a study headed by UCSF, the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Michigan.
Severe restrictions and bans on abortion access may have life-changing and even life-threatening consequences in as many as 28 states for women of childbearing age with conditions like migraine, multiple sclerosis (MS) and epilepsy.
A new study shows that when residents in Black communities have a stroke, they are at greater risk of receiving care at a less-resourced hospital, where their chances of recovery are slimmer.
In a new study of Alzheimer’s disease, UCSF reserachers have discovered that a relatively unstudied form of the tau protein associated with neurodegeneration may be a means for better diagnosis and treatment of the disease.