Research at UC San Francisco has shown for the first time how the commonly prescribed seizure and pain medication, gabapentin, acts inside of cells, opening the door to new, more effective treatments for diseases like epilepsy and Lupus.
The twin papers, published in Nature on May 17 and Nature Structural and Molecular Biology on March 27, show how gabapentin interacts with ion channels called voltage-gated calcium channels, which are critical to the function of numerous organs, from the heart to the brain to the gut.
We have shown how gabapentin binds to calcium channels, giving the field the opportunity to design a new generation of therapies.
“Gabapentin is a very important, widely used drug, but it has many side effects, including dizziness and nausea, and we don’t understand how it works,” said Daniel Minor, PhD, a biophysics professor in the UCSF Cardiovascular Research Institute and the senior author of both papers. “We have shown how gabapentin binds to calcium channels, giving the field the opportunity to design a new generation of therapies.”
Ion channels are molecular pores that control the flow of ions – electrically-charged atoms, like calcium – in and out of the cell. While many drugs have been developed to open or block calcium channels, gabapentin binds to these channels without affecting their ability to ferry calcium, posing a mystery for the drug’s potent effects.
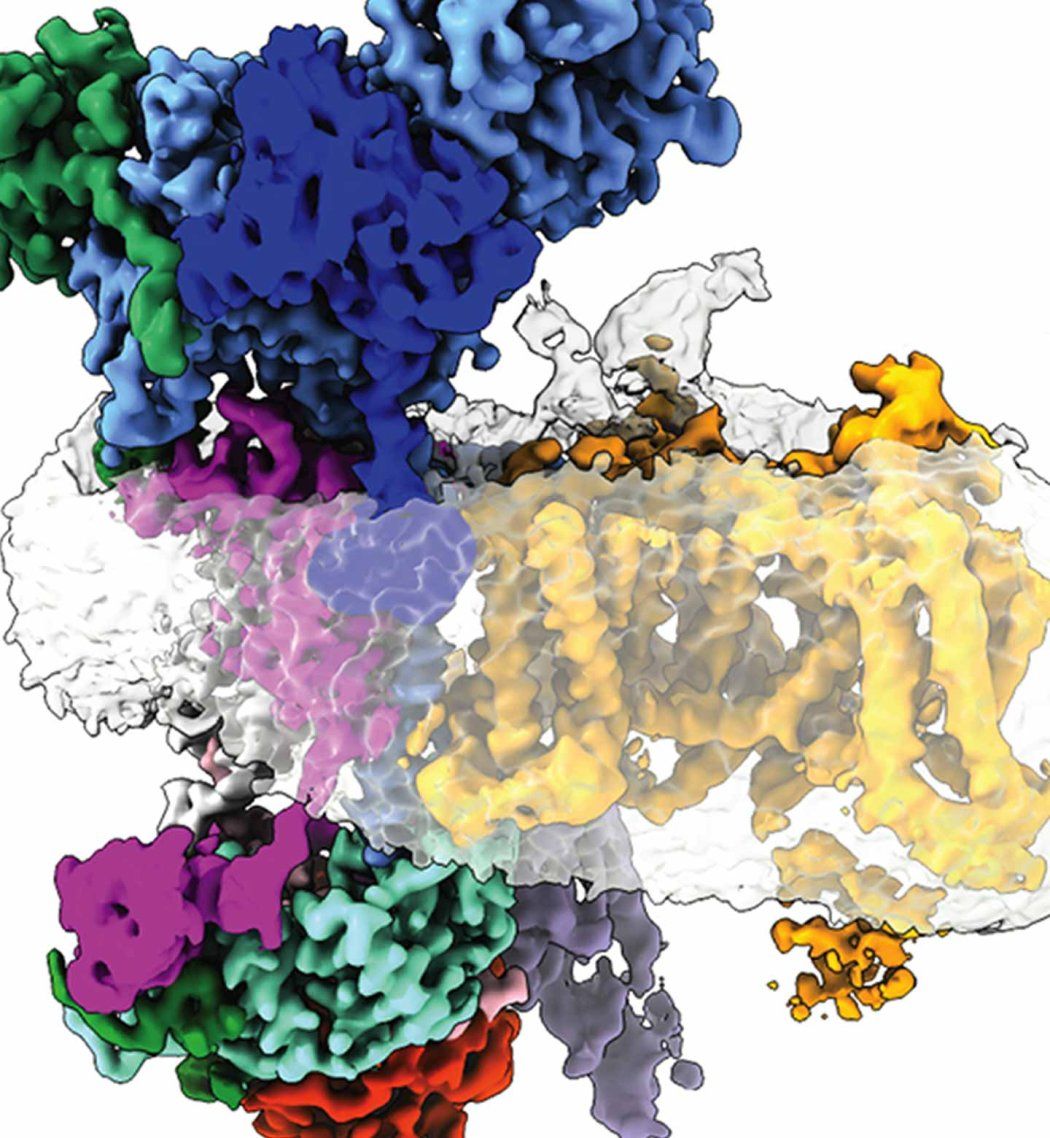
To address this mystery, Minor and his colleagues first mapped exactly where this interaction occurred in 3D, confirming gabapentin’s landing site on a seemingly innocuous part, or subunit, of the calcium channel. But then they spotted a strange, secondary character – a crescent-shaped protein – that bound to a separate subunit of the channel. Crucially, this only occurred in the absence of the gabapentin-binding subunit.
With the help of the neighboring UCSF lab of Balyn Zaro, PhD, the group discovered that this crescent was a protein known as EMC. First identified in 2009 by other scientists at UCSF, EMC is an enzyme that holds pieces of proteins together as they’re being prepared for installation on the outside of cells. Minor and his colleagues had caught EMC in the act of holding partially-built ion channels – a first. And they realized that gabapentin may interfere with that process.
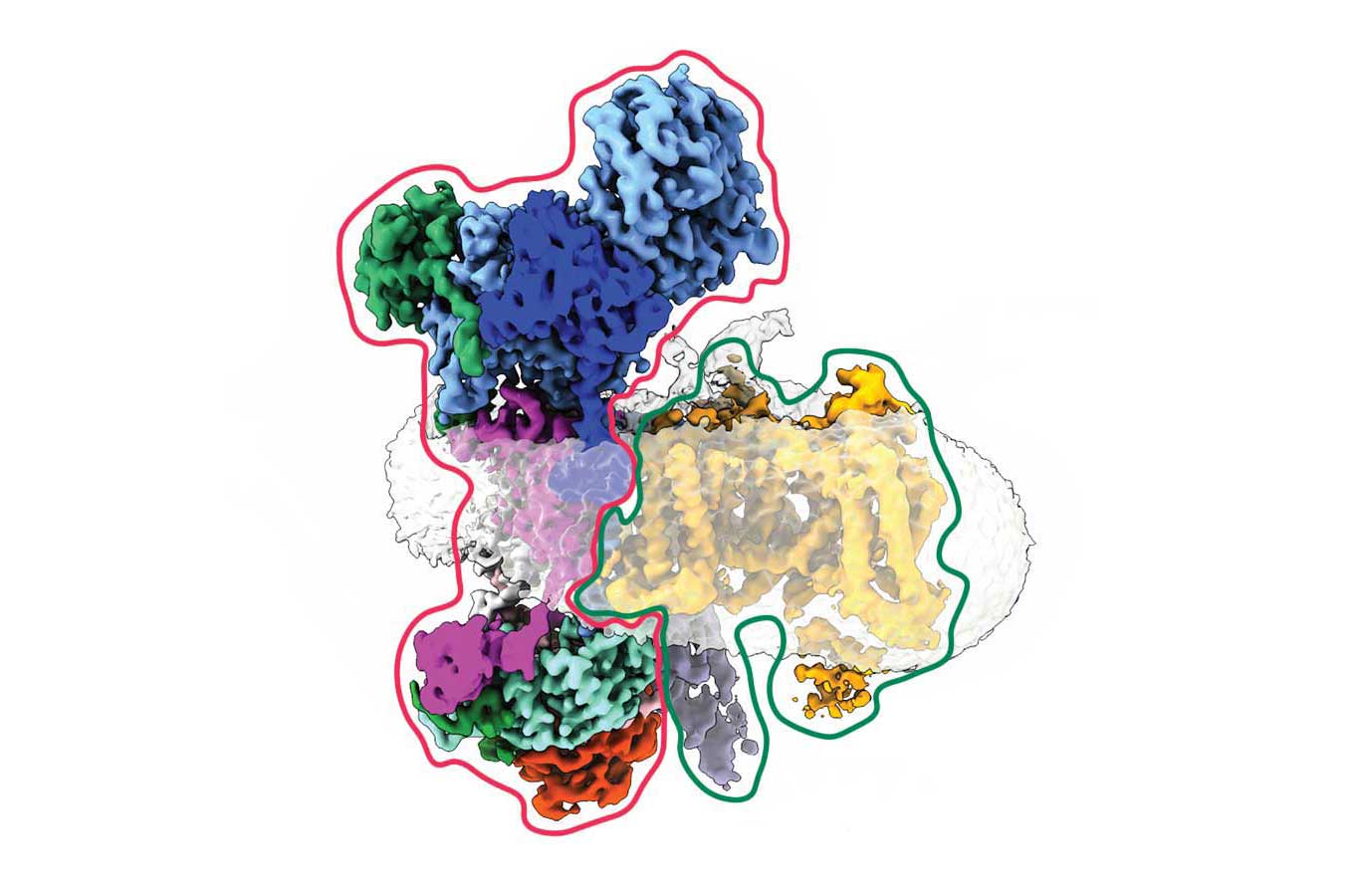
“Gabapentin affects channel biogenesis, and its job is to either block assembly or do something that regulates the number of channels on the cell surface,” said Minor. This, in turn, could change how much calcium gets into a cell, he explained, perhaps soothing a hyperactive brain during epilepsy or bouts of pain.
Minor is hopeful that a wider array of therapies can be developed based on this new understanding of the importance of ion channel construction, in addition to ion channel function. Especially for hard-to-treat conditions like epilepsy, the more therapeutic options, the better, he said.
“We’ve never been able to observe channel assembly, but we now see that we can intervene in this process with a drug that’s very effective for treating pain,” Minor said. “This breaks the field wide open.”