Science in Focus: Regenerating Muscle from Stem Cells
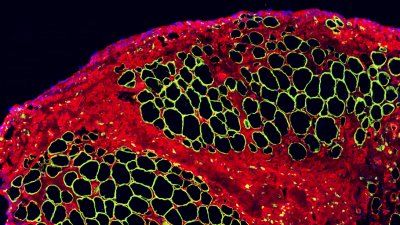
A microscopic image of a mouse leg that has been reconstructed with a stem cell transplant shows what may one day help patients regrow new muscle after a major surgery.
University of California San Francisco
Give to UCSFA microscopic image of a mouse leg that has been reconstructed with a stem cell transplant shows what may one day help patients regrow new muscle after a major surgery.

Ophir Klein has been awarded one of two inaugural grants from the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research that are meant to encourage long-term ambitious and innovative research.

Researchers at UCSF have discovered a previously unknown mass migration of inhibitory neurons into the brain’s frontal cortex during the first few months after birth.
Ten years after Shinya Yamanaka published his Nobel Prize-winning discovery of induced pluripotent stem cells, there's been rapid progress in some areas and major challenges in others.
Chronic pain and loss of bladder control are among the most devastating consequences of spinal cord injury.
A team of researchers led by UCSF scientists has demonstrated in mice that it is possible to generate healthy new liver cells within the organ itself, making engraftment unnecessary.
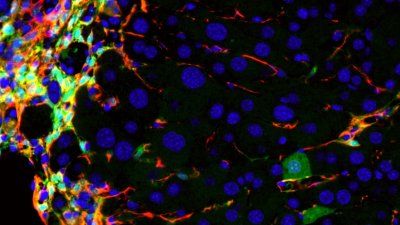
Stem cell biologists at UCSF have demonstrated that IL-1 itself directly transforms the blood system by driving blood stem cells in the bone marrow to switch away from their restorative, rejuvenating role in blood renewal and towards emergency production of immune cells.

Strengthening the link between Zika virus and microcephaly, scientists at UCSF have discovered that a protein the virus uses to infect skin cells and cause a rash is present also in stem cells of the developing human brain and retina.
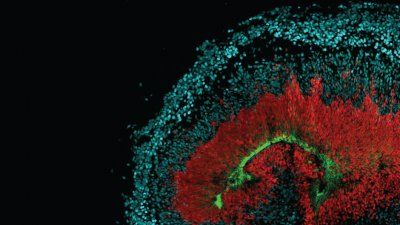
New research by UCSF stem cell biologists has revealed that a DNA-binding protein called Foxd3 acts like a genetic traffic signal, holding that ball of undifferentiated cells in a state of readiness for its great transformation in the third week of development.

We asked experts across UCSF to identify what's ahead in how we approach research, what disease areas will see major advances, and where basic science will be translating into real treatments.

Researchers at UCSF have succeeded in mapping the genetic signature of a unique group of stem cells in the human brain that seem to generate most of the neurons in our massive cerebral cortex.

UCSF scientists describe capturing and studying individual metastatic cells from human breast cancer tumors implanted into mice as the cells escaped into the blood stream and began to form tumors elsewhere in the body.

Zev Gartner is working to building a fully functioning 3-D human breast tissue that will allow him to test potential cancer therapies, an innovation that's earned him a spot among Popular Science's "Brilliant 10" this year.
